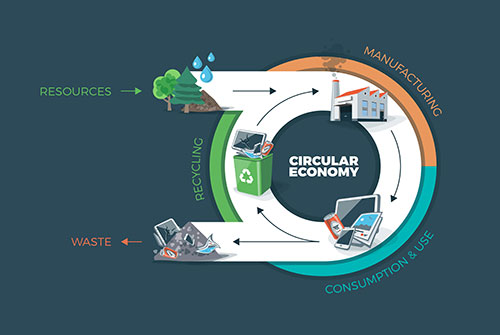
The Circular Economy (CE) approach is one that is being adopted across the world due to many advantages associated with it.
However, for the sake of this article, which considers the agricultural value chain; one of the major motivations behind adopting a CE approach is resource efficiency. For example, the Union Government is exploring how the linear1 economy can transition to a circular economy and has chosen eleven end-of-life products/recyclable materials/wastes of which agricultural waste has been allocated to the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare as the concerned line Ministry. From the examples that will be described below, it will be conveyed that the circular economy approach has significant implications on the addressal of Food Loss and Waste.
Let us consider some examples of how multinational companies are adopting a circular economy approach in their business operations. One company is Sodexo, which has introduced the WasteWatch2 powered by Leanpath Program, whereby Sodexo teams can rapidly and easily capture food waste data, giving clear insights into what is being wasted in their kitchens and why. Furthermore, many MNCs are applying circular economy principles in relation to the usage of plastics. Consider the New Plastics Economy, which is an initiative by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, and which has FMCG giants such as Nestle, the Coca Cola Company, Danone, Mars Inc. and Unilever as partners, amongst others. Furthermore, the circular economy approach is a means for agri-businesses to address to meet global commitments that align with Agenda 2030, namely SDG 12 (Sustainable Production and Consumption).
Let us consider how circular economy approaches are used by actors along the agricultural value chain. Traders at Hyderabad’s Bowenpally sabzi mandi have installed a biogas plant on the premises, which is an example of the usage of waste-to-energy converters by the conversion of vegetable3 waste into electricity. According to the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, such technology applies two principles of a Circular Economy, which includes “Design Out Waste and Pollution” and “Keep Products and Materials in Use.” Further downstream, a circular economy approach is demonstrated by food banks, which are focused on the recovery and distribution of food to areas of need. This particularly played an important role during the outbreak of the COVID19 pandemic when supply chains and incomes were impacted and affected access to food. This model is important to be noted as it involves the private sector participation, namely major MNCs, which under CSR are approached for donations, namely, of the packaged and processed food kind.
In conclusion, adopting a circular economy is part of a multi-step approach towards facilitating the development of sustainable food systems.